What to Know About Crypto Exchange Fees sets the stage for a deep dive into the world of cryptocurrency trading costs, offering a fresh and insightful take that will keep you hooked from start to finish.
Get ready to uncover the nitty-gritty details that can make or break your trading game.
Overview of Crypto Exchange Fees: What To Know About Crypto Exchange Fees
Cryptocurrency exchange fees are charges incurred when buying, selling, or trading digital assets on a crypto exchange platform. These fees are essential for the operation of the exchange and can vary based on the platform and the type of transaction being conducted. It is crucial for traders to understand these fees to make informed decisions and maximize their profits.
Types of Crypto Exchange Fees
- Trading Fees: These are fees charged for executing a trade on the platform. They are usually a percentage of the total transaction amount.
- Deposit and Withdrawal Fees: Some exchanges charge fees for depositing or withdrawing funds from the platform. These fees can vary based on the payment method used.
- Maker and Taker Fees: Maker fees are charged to traders who provide liquidity to the market by placing limit orders. Taker fees are charged to traders who take liquidity from the market by placing market orders.
Understanding these different types of fees can help traders calculate the total cost of their transactions and choose the most cost-effective options when trading cryptocurrencies.
Common Types of Crypto Exchange Fees
![]()
When trading cryptocurrencies on exchanges, users often encounter various types of fees that can impact their overall profits. It’s essential to understand these fees to make informed decisions and optimize trading strategies.
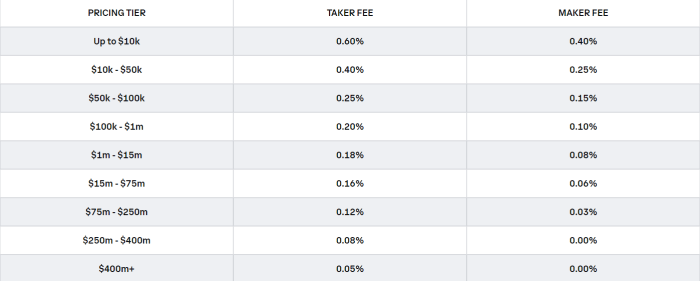
Maker vs. Taker Fee Structure
The maker vs. taker fee structure is a common fee model used by crypto exchanges. Makers are traders who create liquidity by placing limit orders on the order book, while takers are traders who remove liquidity by placing market orders. Exchanges typically charge lower fees for makers than takers to incentivize liquidity provision. This fee structure can impact traders depending on their trading style and frequency.
Withdrawal Fees, What to Know About Crypto Exchange Fees
Withdrawal fees are charges imposed by exchanges when users move their cryptocurrencies off the platform. These fees can vary significantly across different exchanges and are usually based on the type of cryptocurrency being withdrawn. Some exchanges offer fixed withdrawal fees, while others calculate fees based on network congestion and transaction size. It’s essential for users to consider withdrawal fees when choosing an exchange to minimize costs.
Trading Fees, Deposit Fees, and Miscellaneous Charges
In addition to maker and taker fees, exchanges may also charge trading fees, deposit fees, and other miscellaneous charges. Trading fees are fees incurred when executing trades on the platform and can vary based on trading volume and membership level. Deposit fees are charges applied when users fund their accounts with fiat currency or cryptocurrencies. Miscellaneous charges may include fees for services like margin trading, lending, or API access. It’s crucial for traders to be aware of all potential fees to accurately calculate their trading costs and maximize their profits.
Factors Influencing Fee Calculation
When it comes to crypto exchange fees, there are several factors that can influence how much you end up paying. Let’s dive into some key aspects that play a role in fee calculation.
Trading Volume Impact
- Exchanges often offer tiered fee structures based on the trading volume of users. The more you trade, the lower the fees you may be charged per transaction.
- High-volume traders may qualify for discounted rates, incentivizing them to trade more frequently on the platform.
- Some exchanges even have special programs for institutional traders with large trading volumes, providing them with personalized fee structures.
Cryptocurrency Type Influence
- The type of cryptocurrency being traded can also impact the fee structure set by exchanges. Different cryptocurrencies may have varying fee levels based on factors such as network congestion or market demand.
- Popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum may have lower fees due to their high liquidity and trading volume compared to lesser-known altcoins.
- Exchanges may adjust fees based on the volatility and risk associated with a particular cryptocurrency, affecting the costs of trading those assets.
Promotional Offers and Discounts
- Some exchanges run promotional campaigns or offer discounts on trading fees to attract new users or encourage increased trading activity.
- Discounts may be provided for users who hold a certain amount of the exchange’s native token or participate in specific trading competitions.
- Exchanges may also introduce limited-time offers or fee waivers for certain trading pairs to promote new listings or boost liquidity in the market.
Strategies to Minimize Crypto Exchange Fees
When it comes to trading cryptocurrencies, minimizing exchange fees is crucial to maximizing your profits. Here are some strategies to help you reduce these costs and choose the right exchange for your needs.
Utilize Maker-Taker Fee Models
Many exchanges use a maker-taker fee model, where makers (those who add liquidity to the market) pay lower fees compared to takers (those who remove liquidity). By strategically placing limit orders instead of market orders, you can take advantage of these lower fees.
Consider Fee Discounts
Some exchanges offer fee discounts based on trading volume or holding their native tokens. By understanding these discount structures and adjusting your trading habits accordingly, you can save significantly on fees over time.
Compare Fee Structures
Before committing to an exchange, thoroughly compare fee structures across different platforms. Look not only at the trading fees but also withdrawal fees, deposit fees, and any other hidden costs that may impact your overall profitability.
Opt for Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operate without a central authority, which often results in lower fees compared to centralized exchanges. While DEXs may have lower liquidity and slower transaction speeds, they can be a cost-effective option for certain trading activities.