Understanding How Crypto Taxes Work sets the stage for unraveling the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation, shedding light on key concepts and practices that govern this evolving landscape. As we delve into the realm of crypto taxes, prepare to embark on a journey that demystifies the intricacies of reporting, implications of mining, regulatory environments, and more.
Get ready to decode the nuances of crypto taxes and equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate this digital financial terrain with confidence and clarity.
Overview of Crypto Taxes

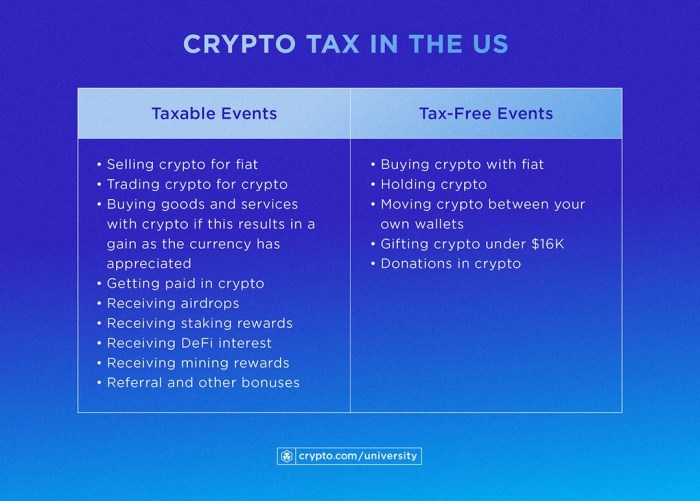
Cryptocurrency taxes refer to the taxation of transactions involving digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. These taxes are important because they ensure that individuals and businesses are compliant with tax laws and regulations set forth by the government.
Taxable Events in the Crypto Space
- Trading one cryptocurrency for another (e.g., BTC for ETH) is considered a taxable event.
- Using cryptocurrency to purchase goods or services is also a taxable event.
- Earning cryptocurrency through mining or staking activities is subject to taxation.
Capital Gains vs. Ordinary Income in Crypto Taxation
Capital gains in crypto taxation are the profits made from selling cryptocurrencies after holding them for a certain period. These gains are taxed at different rates depending on how long the assets were held.
On the other hand, ordinary income in crypto taxation includes earnings from activities like mining, staking, or receiving cryptocurrencies as payment for services rendered. This income is taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate.
Reporting Crypto Transactions: Understanding How Crypto Taxes Work
When it comes to reporting crypto transactions for tax purposes, it’s crucial to keep accurate records and understand how to calculate gains or losses from your crypto trades. This process can seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid any penalties.
Calculating Gains or Losses
- Calculate the difference between the purchase price and the selling price of your crypto assets to determine your gains or losses.
- Consider other factors such as transaction fees, mining rewards, and airdrops when calculating your overall profits or losses.
- Use the FIFO (First In, First Out) method or specific identification method to determine which assets are being sold to accurately calculate gains or losses.
Importance of Record-Keeping
- Maintain detailed records of all your crypto transactions, including dates, amounts, prices, and other relevant information.
- Keep track of your trading activities across different platforms and wallets to ensure accurate reporting to the IRS.
- Record any transfers between wallets, exchanges, or other parties to have a complete history of your crypto transactions for tax purposes.
Tax Implications of Mining and Staking
Mining and staking in the crypto world can have significant tax implications that individuals need to be aware of. Let’s dive into how these activities are taxed and what income is generated through them.
Income Generated through Mining and Staking
When you mine or stake cryptocurrencies, the income generated is considered as ordinary income for tax purposes. This means that you need to report the value of the coins earned as income on your tax return. The value is typically determined based on the fair market value of the coins at the time they were received.
Deductions and Allowances for Miners and Stakers, Understanding How Crypto Taxes Work
As a miner or staker, you may be eligible for certain deductions and allowances to reduce your tax liability. Some common deductions include expenses related to mining equipment, electricity costs, and any fees paid to mining pools. These expenses can be deducted from your mining or staking income, lowering the amount of taxable income you have to report.
It’s important to keep detailed records of your mining and staking activities, including the value of coins earned, expenses incurred, and any other relevant information. By staying organized and informed about the tax implications of mining and staking, you can ensure compliance with tax laws and optimize your tax situation.
Regulatory Environment for Crypto Taxes
Cryptocurrency taxation is a complex and evolving area, with regulations varying from country to country. It is crucial for individuals and businesses to understand and comply with the tax laws governing crypto transactions to avoid legal issues and penalties.
Current Regulatory Landscape
In the United States, the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property for tax purposes. This means that capital gains tax applies to any profits made from buying, selling, or trading crypto. Failure to report these transactions accurately can lead to audits and fines.
International Perspectives
Different countries have different approaches to taxing cryptocurrencies. For example, in Japan, crypto profits are subject to income tax, while in Germany, crypto holdings are tax-free if held for over a year. It’s important to research and understand the tax laws in your specific country to ensure compliance.
Importance of Compliance
Staying compliant with tax laws when dealing with cryptocurrencies is essential to avoid legal consequences. The IRS has been increasing its efforts to track crypto transactions and enforce tax regulations. Keeping detailed records of all crypto transactions and accurately reporting them on your tax returns is crucial to staying on the right side of the law.