Difference Between Bitcoin and Ethereum takes center stage, inviting readers on a journey through the world of cryptocurrencies. Get ready to explore the unique features and functionalities of these two giants in the digital realm.
Introduction to Bitcoin and Ethereum
Bitcoin and Ethereum are two of the most popular cryptocurrencies in the world, each with its unique features and functions.
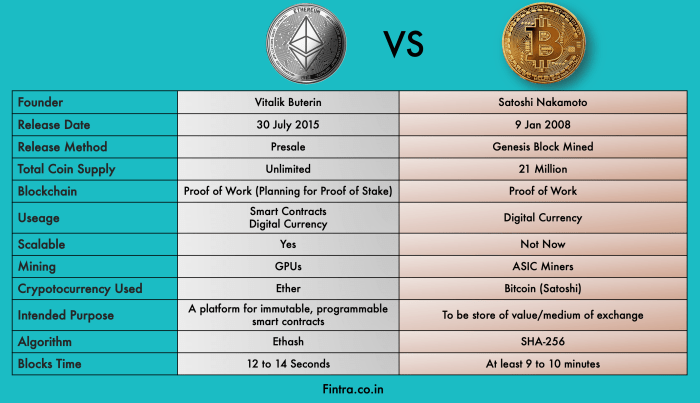
Bitcoin, created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, is the first decentralized digital currency. It operates without a central authority or banks, making it a peer-to-peer system for transactions. Bitcoin’s main purpose is to enable secure, anonymous, and transparent transactions.
Ethereum, on the other hand, was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and development began in early 2014, with the network going live on July 30, 2015. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum is a platform that enables developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) using smart contracts. Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency is called Ether, which is used to fuel transactions on the network.
Both Bitcoin and Ethereum have made significant impacts in the world of cryptocurrency, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the digital financial space. Their popularity and adoption have paved the way for the rise of numerous other cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects.
Technology and Purpose
Bitcoin and Ethereum both utilize blockchain technology, a decentralized and distributed ledger system that ensures transparency and security in transactions. However, they have different underlying technologies and purposes.
Bitcoin: Digital Currency/Store of Value
Bitcoin was created as a digital currency and a store of value, allowing users to make peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Its primary purpose is to provide a secure and efficient way to transfer value globally.
- Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the blockchain, a public ledger that maintains a record of all transactions.
- Bitcoin mining, the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, is done by specialized computers solving complex mathematical problems.
- Bitcoin has a limited supply cap of 21 million coins, making it a deflationary asset and a potential hedge against inflation.
Ethereum: Decentralized Platform for Smart Contracts
Ethereum, on the other hand, was designed as a decentralized platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Its main purpose is to enable developers to build and deploy smart contracts on the blockchain.
- Ethereum transactions are also recorded on the blockchain, but it allows for the execution of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- Ethereum uses a cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH) to power the network and execute smart contracts.
- Ethereum’s flexibility and programmability make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications beyond digital currencies, including decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Usage in the Digital Landscape
Bitcoin is primarily used as a digital currency for transactions and as a store of value for long-term investment. On the other hand, Ethereum is used for a variety of applications beyond just financial transactions, thanks to its smart contract capabilities.
Scalability and Transaction Speed
Bitcoin’s scalability has been a point of contention, with its limited block size and slower transaction speeds leading to congestion on the network during periods of high demand. Ethereum has been working on solutions like Ethereum 2.0 to address scalability issues and improve transaction speeds.
Overall, while Bitcoin and Ethereum both operate on blockchain technology, their purposes and use cases differ significantly, catering to different needs in the digital landscape.
Mining and Consensus Mechanism: Difference Between Bitcoin And Ethereum
Bitcoin and Ethereum both rely on mining and consensus mechanisms to validate transactions on their respective networks.
Mining Process
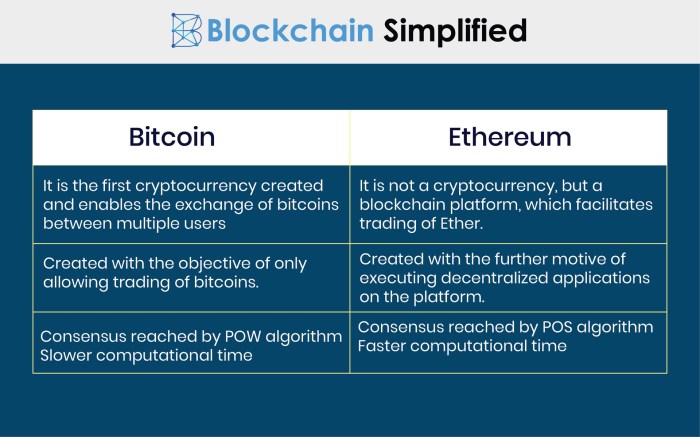
- Bitcoin: In Bitcoin mining, miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins.
- Ethereum: Ethereum mining is similar to Bitcoin but uses a different hashing algorithm called Ethash. Miners compete to find the solution to a cryptographic puzzle and the winner adds a new block to the Ethereum blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms, Difference Between Bitcoin and Ethereum
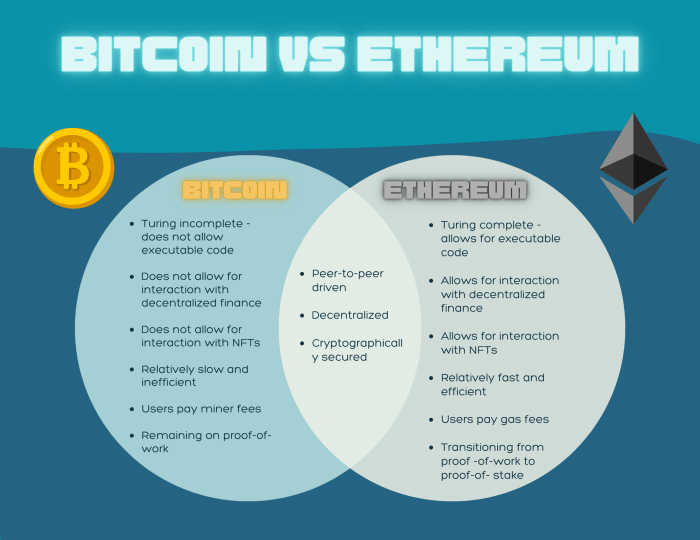
- Bitcoin: Bitcoin uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, where miners compete to solve puzzles and validate transactions. This process ensures security and decentralization but requires significant energy consumption.
- Ethereum: Ethereum is transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold, reducing energy consumption and increasing scalability.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
- Bitcoin: Due to its PoW mechanism, Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to concerns about its environmental impact. The process of mining requires specialized hardware and consumes electricity on a large scale.
- Ethereum: As Ethereum transitions to PoS, the energy consumption is expected to decrease significantly compared to Bitcoin. PoS is more energy-efficient as it does not rely on solving complex puzzles but rather on staking coins for validation.
Development and Upgrades
When it comes to the development and upgrades of Bitcoin and Ethereum, both cryptocurrencies have vibrant communities working behind the scenes to improve their platforms and functionalities.
Development Communities
- Bitcoin: The Bitcoin community is known for its decentralized nature, with various developers contributing to the open-source code. Key figures include developers like Gavin Andresen and Wladimir J. van der Laan.
- Ethereum: Ethereum has a strong development community led by the Ethereum Foundation. Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, plays a significant role in guiding the development of the platform.
Upgrade Processes
- Bitcoin: Bitcoin upgrades primarily take the form of forks, where changes to the protocol are implemented. Examples include the controversial Bitcoin Cash fork in 2017.
- Ethereum: Ethereum undergoes hard forks and network upgrades to implement changes and improvements. Notable upgrades include the Byzantium and Constantinople hard forks.
Governance Models
- Bitcoin: Bitcoin’s governance model is decentralized, with decisions made through rough consensus among miners, developers, and users. There is no formal governance structure in place.
- Ethereum: Ethereum’s governance model involves key stakeholders like developers, miners, and users who participate in decision-making processes. The Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) process helps in proposing and implementing changes.
Future Roadmap and Developments
- Bitcoin: The future roadmap for Bitcoin includes improvements in scalability, privacy, and security. Initiatives like the Lightning Network aim to enhance transaction speeds and reduce fees.
- Ethereum: Ethereum is working towards transitioning to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. This upgrade aims to improve scalability and energy efficiency.